Red neuronal profunda optimizada para la clasificación de psoriasis de alta precisión a partir de imágenes dermatoscópicas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/rcsi.v5i2.996Palabras clave:
enfermedad de la piel, memoria a corto plazo, psoriasis, red eficienteResumen
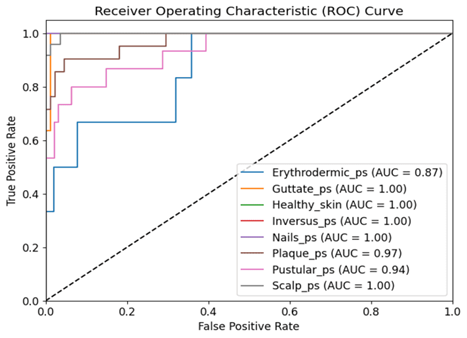
La clasificación precisa de la psoriasis es crucial en el diagnóstico dermatológico debido a las diversas presentaciones clínicas de la enfermedad y sus distintos niveles de gravedad. Con numerosos subtipos y sus similitudes visuales con otras afecciones dermatológicas, un diagnóstico preciso generalmente requiere conocimientos médicos especializados. La identificación temprana y precisa de los subtipos de psoriasis es esencial para iniciar un tratamiento oportuno. Este estudio presenta una novedosa arquitectura híbrida de aprendizaje profundo que integra EfficientNet con redes de memoria a largo plazo (LSTM) para la clasificación automatizada de la psoriasis a partir de imágenes dermatoscópicas. El modelo propuesto está diseñado para capturar simultáneamente características espaciales mediante EfficientNet y patrones temporales o secuenciales mediante unidades LSTM, mejorando así el rendimiento de la clasificación. Los modelos se entrenan y prueban en un conjunto de datos de referencia público que comprende siete clases distintas, utilizando el conjunto de datos de referencia disponible públicamente de Dermnet y BFL-NTU. Los resultados experimentales demuestran que la arquitectura propuesta supera significativamente a los modelos de referencia, como VGG16 y ResNet50, con una precisión superior del 89,7% y un rendimiento robusto en métricas como la recuperación, la puntuación F1 del 88% y la región de convergencia (ROC) del 97%. Este diseño compacto, con bajos parámetros de entrenamiento, reduce el tiempo de cálculo y la memoria, lo que lo hace ideal para su implementación en dispositivos portátiles y permite evaluaciones dermatológicas móviles en tiempo real.
Descargas
Citas
Abbas, M., Arslan, M., Yousaf, F., & Khan, A. A. (2024). Enhanced Skin Disease Diagnosis through Convolutional Neural Networks and Data Augmentation Techniques. Journal of Computing & Biomedical Informatics, 7(1). https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.56979/701/2024
Adegun, A. A., & Viriri, S. (2020). FCN-Based DenseNet Framework for Automated Detection and Classification of Skin Lesions in Dermoscopy Images. IEEE Access, 8, 150377–150396. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016651
Ahmmed, F., Zaheer Raihan, Kamnur Nahar, Asadujjaman, D. M., Mahfujur Rahman, & Abdullah Tamim. (2025). Skin Disease Detection and Classification of Actinic Keratosis and Psoriasis Utilizing Deep Transfer Learning. ArXiv Preprint. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2501.13713
Aijaz, S. F., Khan, S. J., Azim, F., Shakeel, C. S., & Hassan, U. (2022). Deep Learning Application for Effective Classification of Different Types of Psoriasis. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2022, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7541583
Aishwarya, U., Daniel, I. J., & Raghul, R. (2020). Convolutional Neural Network based Skin Lesion Classification and Identification. 2020 International Conference on Inventive Computation Technologies (ICICT), 264–270. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICT48043.2020.9112485
Ayad, H., & Ismail, T. (2020). An Efficient Detection Framework for Linear Skin Lesions with Pigmentary Disorders. 2020 30th International Conference on Computer Theory and Applications (ICCTA), 128–133. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCTA52020.2020.9477657
Azam, S. N. Z. N., Zakaria, N. H., Hassan, R., & Zulkifle, F. A. (2022). Classification of Psoriasis Microarray Data using Machine Learning. 2022 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Cybernetics Technology & Applications (ICICyTA), 245–249. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICyTA57421.2022.10038180
Bolia, C., & Joshi, S. (2024). A Comparative Study of Convolutional Neural Network Architecture for Efficient Classification of Psoriasis Disease (pp. 157–171). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-4533-3_12
DermNetNZ website. (2022). Image Library. https://dermnetnz.org/image-library
Esteva, A., Kuprel, B., Novoa, R. A., Ko, J., Swetter, S. M., Blau, H. M., & Thrun, S. (2017). Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature, 542(7639), 115–118. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21056
Graves, A., & Schmidhuber, J. (2005). Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Networks, 18(5–6), 602–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2005.06.042
Greff, K., Srivastava, R. K., Koutnik, J., Steunebrink, B. R., & Schmidhuber, J. (2017). LSTM: A Search Space Odyssey. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 28(10), 2222–2232. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2582924
Griffiths, C. E., & Barker, J. N. (2007). Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. The Lancet, 370(9583), 263–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3
Hammad, M., Pławiak, P., ElAffendi, M., El-Latif, A. A. A., & Latif, A. A. A. (2023). Enhanced Deep Learning Approach for Accurate Eczema and Psoriasis Skin Detection. Sensors, 23(16), 7295. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23167295
Huang, C., Yu, A., Wang, Y., & He, H. (2020). Skin Lesion Segmentation Based on Mask R-CNN. 2020 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Visualization (ICVRV), 63–67. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICVRV51359.2020.00024
Jagannathan, V., Priya, R., Sundararajan, V., & Banu, M. (2024). CNN–BiGRU-based hybrid deep learning model for dermatological disease classification. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2024.104006
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., & Hinton, G. E. (2017). ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6), 84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., & Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature, 521(7553), 436–444. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Li, X., & Kong, A. W. K. (2017). A multi-model restoration algorithm for recovering blood vessels in skin images. Image and Vision Computing, 61, 40–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imavis.2017.02.006
Lowes, M. A., Bowcock, A. M., & Krueger, J. G. (2007). Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature, 445(7130), 866–873. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05663
Peng, L., Na, Y., Changsong, D., Sheng, L. I., & Hui, M. (2021). Research on classification diagnosis model of psoriasis based on deep residual network. Digital Chinese Medicine, 4(2), 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcmed.2021.06.003
Pham, T.-C., Doucet, A., Luong, C.-M., Tran, C.-T., & Hoang, V.-D. (2020). Improving Skin-Disease Classification Based on Customized Loss Function Combined With Balanced Mini-Batch Logic and Real-Time Image Augmentation. IEEE Access, 8, 150725–150737. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3016653
Sandler, M., Howard, A., Zhu, M., Zhmoginov, A., & Chen, L.-C. (2018). MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 4510–4520. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00474
Singh, A., Verma, N., & Shukla, S. (2023). Deep learning framework for psoriasis detection using VGG and Inception models.
Tan, M., & Le, Q. V. (2019). EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. 97, 6105–6114. https://doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1905.11946
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Xie, F., & Liu, J. (2025). Enhancing Diagnosis of Psoriasis and Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Spatially Aligned Multimodal Model Integrating Clinical and Dermoscopic Images. Journal of Investigative Dermatology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jid.2025.03.034
Wijesinghe, L., Kulasekera, D., & Ilmini, W. (2019). An Intelligent Approach to Segmentation and Classification of Common Skin Diseases in Sri Lanka. 2019 National Information Technology Conference (NITC), 47–52. https://doi.org/10.1109/NITC48475.2019.9114507
Yang, Y., Wang, J., Xie, F., Liu, J., Shu, C., Wang, Y., Zheng, Y., & Zhang, H. (2021). A convolutional neural network trained with dermoscopic images of psoriasis performed on par with 230 dermatologists. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 139, 104924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104924
Zhu, W., Lai, H., Zhang, H., Zhang, G., Luo, Y., Wang, J., Sun, L., Lu, J., Wang, S., & Xiang, Y. (2024). Abscissa-Ordinate Focused Network for Psoriasis and Eczema Healthcare Cyber-Physical System With Active Label Smoothing. IEEE Access, 12, 54953–54963. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3384310
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2025 Charu Bolia, Sunil Joshi

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores retienen sus derechos:
a. Los autores retienen sus derechos de marca y patente, y tambien sobre cualquier proceso o procedimiento descrito en el artículo.
b. Los autores retienen el derecho de compartir, copiar, distribuir, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente el articulo publicado en la Revista Científica de Sistemas e Informática (RCSI) (por ejemplo, colocarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en la RCSI.
c. Los autores retienen el derecho a hacer una posterior publicación de su trabajo, de utilizar el artículo o cualquier parte de aquel (por ejemplo: una compilación de sus trabajos, notas para conferencias, tesis, o para un libro), siempre que indiquen la fuente de publicación (autores del trabajo, revista, volumen, número y fecha).









