Sistemas de administración tributaria digital: Una revisión de la literatura en Scopus (2012-2022)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/rcsi.v3i2.525Palabras clave:
big data, blockchain, digitalización, sistemas de informaciónResumen
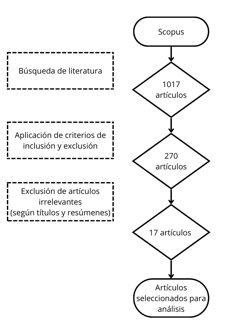
El estudio analizó el uso de tecnologías avanzadas en la gestión fiscal y financiera en instituciones públicas, con énfasis en la implementación de herramientas tecnológicas y los desafíos asociados. A través de una revisión sistemática de 17 artículos científicos indexados en Scopus (2012-2022), se identificaron tecnologías como Blockchain, Sistemas de Información Geográfica (GIS), Big Data, IoT y redes neuronales, destacando su impacto en la eficiencia operativa, la recaudación de impuestos y la detección de fraudes. Los resultados revelan que estas tecnologías han mejorado la automatización de procesos, la toma de decisiones y la seguridad financiera, mientras que la digitalización de procesos aduaneros y fiscales ha optimizado la recolección de datos y la eficiencia presupuestaria. Sin embargo, persisten desafíos en términos de recursos técnicos, interoperabilidad de sistemas y seguridad de los datos. El éxito de la implementación de estas tecnologías depende en gran medida de la capacidad de las instituciones para modernizar sus sistemas existentes y adaptarse a los avances tecnológicos. En conclusión, las tecnologías emergentes ofrecen una oportunidad considerable para transformar la gestión fiscal y financiera en el sector público, aunque será necesario seguir abordando los retos para maximizar su potencial impacto.
Descargas
Citas
Al-Mawali, H., Al Natour, A. R., Zaidan, H., Shishan, F., & Rumman, G. A. (2022). Examining the Factors Influencing E-Tax Declaration Usage among Academics’ Taxpayers in Jordan. Informatics, 9(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9040092
Alanezi, M. A., Mahmood, A. K., & Basri, S. (2012). E-government service quality: A qualitative evaluation in the case of Saudi Arabia. Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 54(1). https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1681-4835.2012.tb00382.x
Alm, J. (2021). Tax evasion, technology, and inequality. Economics of Governance, 22(4), 321–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10101-021-00247-w
Anagnostopoulos, D., Papadopoulos, T., Stamati, T., & Balta, M. E. (2020). Policy and Information Systems Implementation: the Greek Property Tax Information System Case. Information Systems Frontiers, 22(4), 791–802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-018-9887-y
Bassey, E., Mulligan, E., & Ojo, A. (2022). A conceptual framework for digital tax administration - A systematic review. Government Information Quarterly, 39(4), 101754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2022.101754
Buldas, A., Draheim, D., Gault, M., Laanoja, R., Nagumo, T., Saarepera, M., Shah, S. A., Simm, J., Steiner, J., Tammet, T., Tammet, T., & Truu, A. (2022). An Ultra-Scalable Blockchain Platform for Universal Asset Tokenization: Design and Implementation. IEEE Access, 10, 77284–77322. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3192837
Cronin, P., Ryan, F., & Coughlan, M. (2008). Undertaking a literature review: a step-by-step approach. British Journal of Nursing, 17(1), 38–43. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjon.2008.17.1.28059
Deng, H., & Xie, D. (2021). Application of the Tax Policy in the Free-Trade Zone Based on Big Data and Internet of Things Technology. Mobile Information Systems, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3315160
Eom, S.-J., & Lee, J. (2022). Digital government transformation in turbulent times: Responses, challenges, and future direction. Government Information Quarterly, 39(2), 101690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.giq.2022.101690
Jiang, Y., Qin, J., & Khan, H. (2022). The Effect of Tax-Collection Mechanism and Management on Enterprise Technological Innovation: Evidence from China. Sustainability, 14(14), 8836. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14148836
Johar, S., Ahmad, N., Asher, W., Cruickshank, H., & Durrani, A. (2021). Research and Applied Perspective to Blockchain Technology: A Comprehensive Survey. Applied Sciences, 11(14), 6252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11146252
Lutfi, A., Al-Okaily, M., Alsyouf, A., & Alrawad, M. (2022). Evaluating the D&M IS Success Model in the Context of Accounting Information System and Sustainable Decision Making. Sustainability (Switzerland), 14(13). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14138120
Malodia, S., Dhir, A., Mishra, M., & Bhatti, Z. A. (2021). Future of e-Government: An integrated conceptual framework. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 173, 121102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121102
Mu, R., Fentaw, N. M., & Zhang, L. (2022). The Impacts of Value-Added Tax Audit on Tax Revenue Performance: The Mediating Role of Electronics Tax System, Evidence from the Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Sustainability (Switzerland), 14(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/su14106105
Night, S., & Bananuka, J. (2019). The mediating role of adoption of an electronic tax system in the relationship between attitude towards electronic tax system and tax compliance. Journal of Economics, Finance and Administrative Science, 25(49), 73–88. https://doi.org/10.1108/JEFAS-07-2018-0066
Peláez-Repiso, A., Sánchez-Núñez, P., & García Calvente, Y. (2021). Tax Regulation on Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: The Implications for Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc7010098
Politou, E., Alepis, E., & Patsakis, C. (2019). Profiling tax and financial behaviour with big data under the GDPR. Computer Law & Security Review, 35(3), 306–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clsr.2019.01.003
Rocha-Salazar, J.-D.-J., Segovia-Vargas, M.-J., & Camacho-Miñano, M.-D.-M. (2022). Detection of shell companies in financial institutions using dynamic social network. Expert Systems with Applications, 207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117981
Serrano, W. (2020). Genetic and deep learning clusters based on neural networks for management decision structures. Neural Computing and Applications, 32(9), 4187–4211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04231-8
Setyowati, M. S., De Utami, N. sila, Saragih, A. H., & Hendrawan, A. (2020). Blockchain Technology Application for Value-Added Tax Systems. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(4), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6040156
Singh, A., Singh, S. K., Meraj, G., Kanga, S., Farooq, M., Kranjčić, N., Đurin, B., & Sudhanshu. (2022). Designing Geographic Information System Based Property Tax Assessment in India. Smart Cities, 5(1), 364–381. https://doi.org/10.3390/smartcities5010021
Singh, P., Dwivedi, Y. K., Kahlon, K. S., Sawhney, R. S., Alalwan, A. A., & Rana, N. P. (2020). Smart Monitoring and Controlling of Government Policies Using Social Media and Cloud Computing. Information Systems Frontiers, 22(2), 315–337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10796-019-09916-y
Strauss, H., Fawcett, T., & Schutte, D. (2020). Tax risk assessment and assurance reform in response to the digitalised economy. Journal of Telecommunications and the Digital Economy, 8(4), 96–126. https://doi.org/10.18080/JTDE.V8N4.306
Umbach, G., & Tkalec, I. (2022). Evaluating e-governance through e-government: Practices and challenges of assessing the digitalisation of public governmental services. Evaluation and Program Planning, 93, 102118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2022.102118
Uyar, A., Nimer, K., Kuzey, C., Shahbaz, M., & Schneider, F. (2021). Can e-government initiatives alleviate tax evasion? The moderation effect of ICT. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 166, 120597. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120597
Vysochan, O., Vysochan, O., Yasinska, A., & Hyk, V. (2021). Selection of Accounting Software for Small and Medium Enterprises Using the Fuzzy Topsis Method. TEM Journal, 10(3), 1348–1356. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM103-43
Wu, Q., Xu, X., & Lin, R. (2021). Government incentive mechanism of closed-loop supply chain based on information asymmetry. RAIRO - Operations Research, 55(6), 3359–3378. https://doi.org/10.1051/ro/2021124
Xiao, F., Chen, R.-S., Zhang, W., Chen, Y.-C., Lu, S.-Y., Chen, Y.-Q., Xiong, N., & Chen, C.-M. (2019). Design and Analysis of a Strengthen Internal Control Scheme for Smart Trust Financial Service. IEEE Access, 7, 163202–163218. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2945056
Zasko, V., Sidorova, E., Komarova, V., Boboshko, D., & Dontsova, O. (2021). Digitization of the customs revenue administration as a factor of the enhancement of the budget efficiency of the russian federation. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(19). https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910757
Zhang, W., Chen, R.-S., Chen, Y.-C., Lu, S.-Y., Xiong, N., & Chen, C.-M. (2019). An Effective Digital System for Intelligent Financial Environments. IEEE Access, 7, 155965–155976. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2943907
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Jonatan Jesus Cardenas-López

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores retienen sus derechos:
a. Los autores retienen sus derechos de marca y patente, y tambien sobre cualquier proceso o procedimiento descrito en el artículo.
b. Los autores retienen el derecho de compartir, copiar, distribuir, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente el articulo publicado en la Revista Científica de Sistemas e Informática (RCSI) (por ejemplo, colocarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en la RCSI.
c. Los autores retienen el derecho a hacer una posterior publicación de su trabajo, de utilizar el artículo o cualquier parte de aquel (por ejemplo: una compilación de sus trabajos, notas para conferencias, tesis, o para un libro), siempre que indiquen la fuente de publicación (autores del trabajo, revista, volumen, número y fecha).








