A contrastive dual attention framework for enhancing adverse drug event relations extraction
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/rcsi.v5i2.968Keywords:
adverse drug events, biomedical NLP, contrastive learning, dual attention, machine learning, natural language processingAbstract
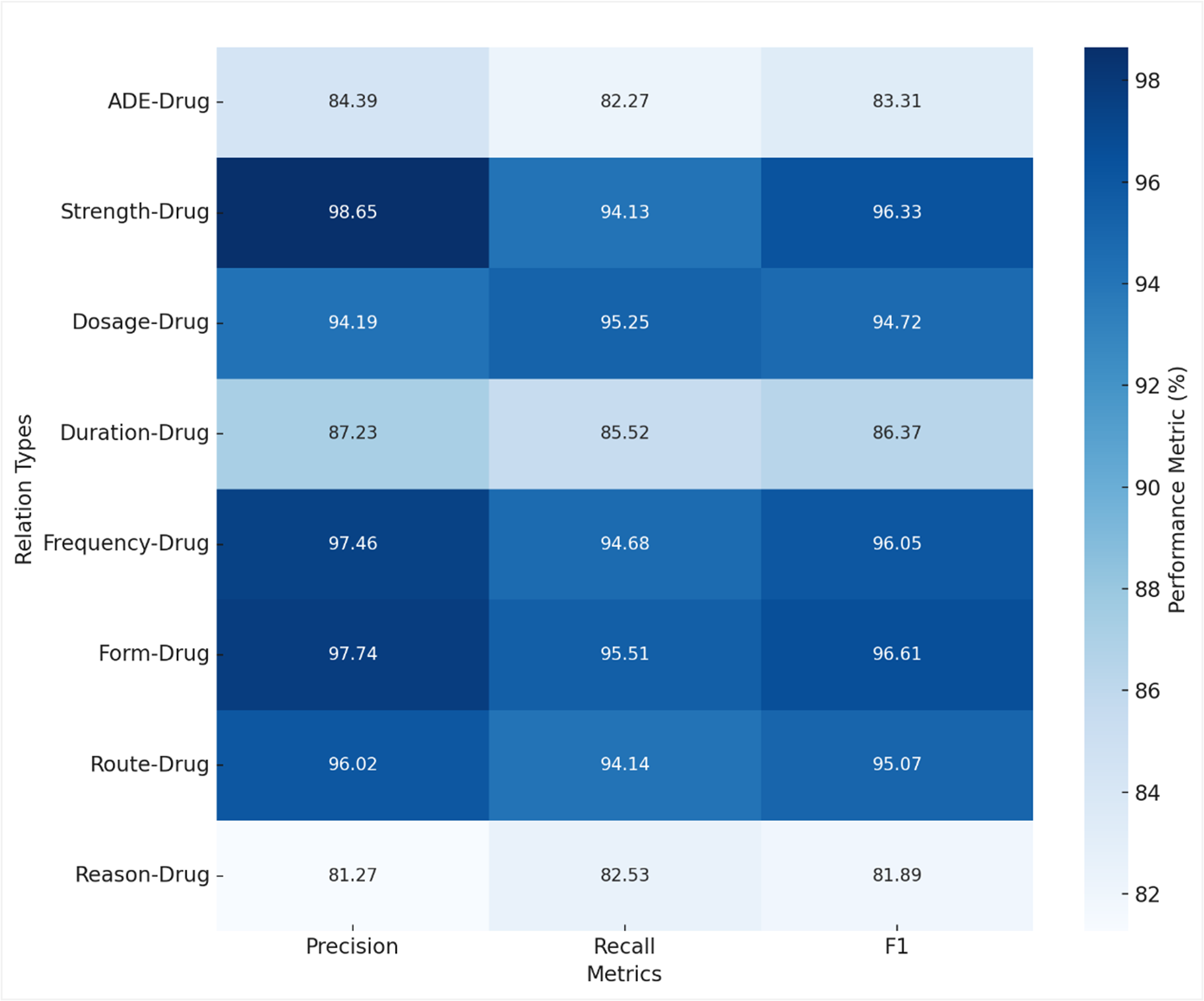
Accurate extraction of relationships between drugs and adverse drug events (ADEs) is essential for improving patient safety. However, current approaches struggle to capture complex relationships due to limitations in contextual representation. In the n2c2 dataset, ADE-Drug instances (1107) are significantly fewer than others such as Strength-Drug (6702) or Reason-Drug (5169), creating a strong class imbalance that hinders identification. A model based on transformer encoders is used to generate contextual embeddings, incorporating a dual attention mechanism that focuses on both the entities and their clinical context. Contrastive learning refines the representation of entity pairs, enabling more precise differentiation between correct and incorrect relationships. Experimental evaluations show a general F1 score of 93.31% and 83.31% for the ADE-Drug relation, outperforming previous methods. The combination of contextual encoding, specialized attention, and contrastive discrimination effectively addresses the challenges of class imbalance and the semantic complexity of clinical language.
Downloads
References
Aguilar-Canto, F., Cardoso-Moreno, M., Jiménez, D., & Calvo, H. (2023). GPT-2 versus GPT-3 and Bloom: LLMs for LLMs Generative Text Detection. CEUR Workshop Proceedings, 3496.
Alsentzer, E., Murphy, J. R., Boag, W., Weng, W.-H., Jin, D., Naumann, T., & McDermott, M. B. A. (2019). Publicly Available Clinical BERT Embeddings. http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.03323
Brown, T. B., Mann, B., Ryder, N., Subbiah, M., Kaplan, J., Dhariwal, P., Neelakantan, A., Shyam, P., Sastry, G., Askell, A., Agarwal, S., Herbert-Voss, A., Krueger, G., Henighan, T., Child, R., Ramesh, A., Ziegler, D. M., Wu, J., Winter, C., … Amodei, D. (2020). Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. http://arxiv.org/abs/2005.14165
Christopoulou, F., Tran, T. T., Sahu, S. K., Miwa, M., & Ananiadou, S. (2020). Adverse drug events and medication relation extraction in electronic health records with ensemble deep learning methods. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(1), 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocz101
Devlin, J., Chang, M.-W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2018). BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. http://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805
El-allaly, E., Sarrouti, M., En-Nahnahi, N., & Ouatik El Alaoui, S. (2021). MTTLADE: A multi-task transfer learning-based method for adverse drug events extraction. Information Processing & Management, 58(3), 102473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102473
Gao, T., Yao, X., & Chen, D. (2021). SimCSE: Simple Contrastive Learning of Sentence Embeddings. http://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08821
Gurulingappa, H., Mateen‐Rajpu, A., & Toldo, L. (2012). Extraction of potential adverse drug events from medical case reports. Journal of Biomedical Semantics, 3(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.1186/2041-1480-3-15
IOM. (2007). Preventing Medication Errors: Quality Chasm Series. En The National Academies Press, Washington, DC. Institute of Medicine.
Ji, Z., Wei, Q., & Xu, H. (2019). BERT-based Ranking for Biomedical Entity Normalization. http://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03548
Johnson, A. E. W., Bulgarelli, L., & Pollard, T. J. (2020). Deidentification of free-text medical records using pre-trained bidirectional transformers. Proceedings of the ACM Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning, 214-221. https://doi.org/10.1145/3368555.3384455
Johnson, A. E. W., Pollard, T. J., Shen, L., Lehman, L. H., Feng, M., Ghassemi, M., Moody, B., Szolovits, P., Anthony Celi, L., & Mark, R. G. (2016). MIMIC-III, a freely accessible critical care database. Scientific Data, 3(1), 160035. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.35
Kim, Y. H., Kim, C., & Kim, Y. S. (2024). Language Model-Based Text Augmentation System for Cerebrovascular Disease-Related Medical Reports. Applied Sciences, 14(19).
Kim, Y., & Meystre, S. M. (2020). Ensemble method–based extraction of medication and related information from clinical texts. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(1), 31-38. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocz100
Kumar, A., Chaudhary, K., Singh, P., & Thapa, J. (2020). Contextual Data Augmentation for Improving Natural Language Understanding in Biomedical Domain. IEEE BIBM.
Lee, J., Yoon, W., Kim, S., Kim, D., Kim, S., So, C. H., & Kang, J. (2019). BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz682
Li, Y., Tao, W., Li, Z., Sun, Z., Li, F., Fenton, S., Xu, H., & Tao, C. (2024). Artificial intelligence-powered pharmacovigilance: A review of machine and deep learning in clinical text-based adverse drug event detection for benchmark datasets. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 152, 104621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2024.104621
Liu, S., Tang, B., Chen, Q., & Wang, X. (2016). Drug-Drug Interaction Extraction via Convolutional Neural Networks. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2016, 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6918381
Modi, S., Kasmiran, K. A., Mohd Sharef, N., & Sharum, M. Y. (2024). Extracting adverse drug events from clinical Notes: A systematic review of approaches used. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 151, 104603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2024.104603
Murphy, S. N., Weber, G., Mendis, M., Gainer, V., Chueh, H. C., Churchill, S., & Kohane, I. (2010). Serving the enterprise and beyond with informatics for integrating biology and the bedside (i2b2). Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 17(2), 124-130. https://doi.org/10.1136/jamia.2009.000893
Peng, Y., Yan, S., & Lu, Z. (2018). Transfer Learning in Biomedical Natural Language Processing: An Evaluation of BERT and ELMo on Ten Benchmarking Datasets. Proceedings of the 18th BioNLP Workshop and Shared Task, 58-65. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/W19-5006
Peng, Y., Yan, S., & Lu, Z. (2020). Biomedical Sentence Similarity Estimation with Transfer Learning and Entity-aware Contrastive Learning. BioNLP Workshop - ACL.
Roberts, K., Demner-Fushman, D., & Tonellato, P. J. (2009). Identifying and classifying adverse drug events in discharge summaries. AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings, 601–605.
Sun, M., Zhang, Z., Han, X., Liu, Z., Jiang, X., & Liu, Q. (2019). ERNIE: Enhanced Language Representation with Informative Entities. http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.07129
Thapa, S., Islamaj, R., Rogers, K., & Demner-Fushman, D. (2022). Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation with Pre-trained Embeddings for Clinical Natural Language Processing: A Case Study on Adverse Drug Event Classification. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 29(6), 1019–1027. https://academic.oup.com/jamia/search-results?page=1&q=TransferLearningandDomainAdaptationwithPre-trainedEmbeddingsforClinicalNaturalLanguageProcessing%3AACaseStudyonAdverseDrugEventClassification&fl_SiteID=5396&SearchSourceType=1&allJ
Vig, J. (2019a). A Multiscale Visualization of Attention in the Transformer Model. http://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05714
Vig, J. (2019b). Visualizing Attention in Transformer-Based Language Representation Models. http://arxiv.org/abs/1904.02679
Wei, Q., Ji, Z., Li, Z., Du, J., Wang, J., Xu, J., Xiang, Y., Tiryaki, F., Wu, S., Zhang, Y., Tao, C., & Xu, H. (2020). A study of deep learning approaches for medication and adverse drug event extraction from clinical text. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(1), 13-21. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocz063
WHO. (2008). The importance of pharmacovigilance - Safety Monitoring of medicinal products. World Health Organization.
Yang, X., Bian, J., Fang, R., Bjarnadottir, R. I., Hogan, W. R., & Wu, Y. (2020). Identifying relations of medications with adverse drug events using recurrent convolutional neural networks and gradient boosting. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, 27(1), 65-72. https://doi.org/10.1093/jamia/ocz144
Zhang, F., Zheng, W., Yu, J., & Qin, Y. (2020). Dual Attention-Based BiLSTM-CNN for Named Entity Recognition.
Zhang, Y., Chen, Q., Yang, Z., Lin, H., & Lu, Z. (2019). BioWordVec, improving biomedical word embeddings with subword information and MeSH. Scientific Data, 6(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-019-0055-0
Zhang, Y., Sun, A., Jin, F., & Zhou, X. (2020). Contrastive learning for text classification. AAAI. http://arxiv.org/abs/2305.09269
Zhou, P., Shi, W., Tian, J., Qi, Z., Li, B., Hao, H., & Xu, B. (2016). Attention-Based Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Relation Classification. Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers), 207-212. https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/P16-2034
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Poonam Kashtriya, Pardeep Singh

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors retain their rights:
a. The authors retain their trademark and patent rights, as well as any process or procedure described in the article.
b. The authors retain the right to share, copy, distribute, execute and publicly communicate the article published in the Revista Científica de Sistemas e Informática (RCSI) (for example, place it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in the RCSI.
c. Authors retain the right to make a subsequent publication of their work, to use the article or any part of it (for example: a compilation of their works, notes for conferences, thesis, or for a book), provided that they indicate the source of publication (authors of the work, journal, volume, number and date).








