Coagulation effect-flocculation in removal of iron and manganese in aquifer
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/reacae.v2i1.464Keywords:
water, coagulants, flocculants, parametersAbstract
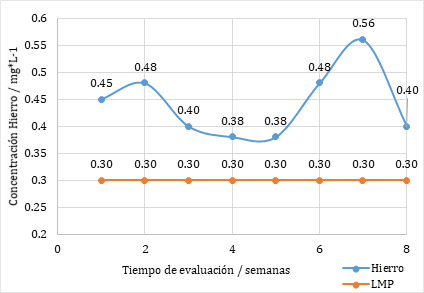
In the district of Yantaló, Moyobamba, there is an aquifer that supplies water as an environmental service to the community, it presents evidence of a high concentration of iron and manganese indicating contamination by heavy metals. The objective was to determine the effect of the coagulation-flocculation process on the removal of iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) in the aquifer. It was hypothesized that the coagulation - flocculation process favors the removal of iron and manganese, being the applied research, whose design was pre-experimental. The aquifer was divided into five zones, taking 20 samples and using the Jar Test method. The initial results showed that the iron concentration exceeded the Maximum Permissible Limits (MLP) of water for human consumption; after applying the independent variable, iron concentrations decreased to 0.3 mg Fe/L. Concluding that after the coagulation - flocculation process through the optimal dose of aluminum sulfate at 1% mother solution, the final parameters remain within the expected range. The optimal dosage design of the Coagulant - Flocculant for the conventional treatment of aquifer water is proposed.
Downloads
References
Álvarez Bastida, C. (2018). Impacto del carácter corrosivo iónico y por dióxido de carbono del agua en materiales de acero al carbón de un sistema de abastecimiento de agua potable en el Municipio de Toluca [Universidad Autónoma del Estado de México]. http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11799/94960
Bora, A. J., Mohan, R., & Dutta, R. K. (2018). Simultaneous removal of arsenic, iron and manganese from groundwater by oxidation-coagulation-adsorption at optimized pH. Water Supply, 18(1), 60–70. https://doi.org/10.2166/ws.2017.092
Chang-Long, F., Liu, C., YU, M.-Y., Chen, S.-Q., & Mehmood, T. (2022). Removal performance and mechanism of the dissolved manganese in groundwater using ultrafiltration coupled with HA complexation. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 10(6), 108931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108931
Cruz Monzon, J. A., Padilla Guzman, M., & Azabache Liza, Y. F. (2011). Efecto del proceso de coagulación floculación, en la remoción del hierro (II), presente en las aguas de la quebrada Juninguillo, Moyobamba [Universidad Nacional de San Martín]. http://hdl.handle.net/11458/2821
Decreto Supremo N.° 031-2010-SA. (2010). Reglamento de la Calidad del Agua para Consumo Humano. Ministerio de Salud (26 de Setiembre de 2010). https://www.gob.pe/institucion/minsa/normas-legales/244805-031-2010-sa
Decreto Supremo N.°015-2015-MINAM. (2015). Modifican los Estándares Nacionales de Calidad Ambiental para Agua y establecen dis-posiciones complementarias para su aplicación. Ministerio Del Ambiente (19 de Diciembre de 2015). https://www.minam.gob.pe/disposiciones/decreto-supremo-n-015-2015-minam/
Du, X., Liu, G., Qu, F., Li, K., Shao, S., Li, G., & Liang, H. (2017). Removal of iron, manganese and ammonia from groundwater using a PAC-MBR system: The anti-pollution ability, microbial population and membrane fouling. Desalination, 403, 97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2016.03.002
Galindo Yantas, G. (2018). Determinación de la dosis óptima de sulfato de aluminio granulado tipo b en la planta de tratamiento de agua potable Yurajhuanca – emapa Pasco [Universidad Nacional Daniel Alcides Carrión]. http://repositorio.undac.edu.pe/handle/undac/347
Guillen-Rivas, J. R., Jaramillo-Cedeño, A. R., Baquerizo-Crespo, R. J., & Córdova-Mosquera, R. A. (2021). Estudio de los procesos de remoción de hierro y manganeso en aguas subterráneas: una revisión. Polo Del Conocimiento, 6(9), 1384–1407. https://doi.org/10.23857/pc.v6i9.3118
Hernández González, S., Gómez Vega, A., Juárez Yáñez, P., & Hernández Zárate, G. (2017). Determinación de hierro y manganeso en el agua subterránea del municipio de Apan, Hidalgo, México. Revista de Divulgación Científica, 5(1). http://reaxion.utleon.edu.mx/Art_Determinacion_de_hierro_y_manganeso_en_el_agua_subterranea_del_municipio_de_Apan_Hidalgo_Mexico.html#
Hernández Sampieri, R., Fernández Collado, C., & Baptista Lucio, M. del P. (2014). Metodología de la Investigación (6th ed.). Interamericana editores, S.A.
Kang, H., Liu, Y., Li, D., & Xu, L. (2022). Study on the Removal of Iron and Manganese from Groundwater Using Modified Manganese Sand Based on Response Surface Methodology. Applied Sciences, 12(22), 11798. https://doi.org/10.3390/app122211798
PNUD. (2015). Objetivos de desarrollo sostenible - Objetivo 6: Agua Limpia y Saneamiento. Programa de las Naciones Unidas para el Desarrollo. https://www.undp.org/es/sustainable-development-goals#agua-limpia-saneamiento
Ruiz Martínez, A., & Coronado Coronel, M. (2016). Tratamiento de agua subterránea mediante la utilización de ósmosis inversa para consumo familiar en el sector Chuina, Morales-San Martín-2015. Revista de Investigación Ciencia, Tecnología y Desarrollo, 2(2), 1.10. https://revistas.upeu.edu.pe/index.php/ri_ctd/article/view/621/0
Sandoval Salazar, N. R., Bravo Mori, J., & Iñapi Bardalez, E. (2020). Mejoramiento del sistema de agua potable de la localidad de Yantaló provincia de Moyobamba región San Martin [Universidad Nacional de San Martín]. http://hdl.handle.net/11458/4254
SENA. (2020). Operación y mantenimiento de tratamiento de agua residual. Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje. https://normograma.sena.edu.co/normograma/docs/arbol/1000.htm
Sierra Ramírez, C. A. (2021). Calidad del agua: Evaluación y diagnóstico (1st ed.). Ediciones de la U.
Swistock, B., & William Sharpe, P. D. (2019). Iron and Manganese in Private Water Systems. In Private well water in connecticut (pp. 1–4). PennState Extension. https://extension.psu.edu/iron-and-manganese-in-private-water-systems
UNESCO. (2021). Informe de las Naciones Unidas sobre el desarrollo de los recursos hídricos 2021: El valor del agua (1st ed.). Organización de las Naciones Unidas para la Educación, la Ciencia y la Cultura.
Valeriano-Mamani, J. J., & Matos-Chamorro, R. A. (2019). Influencia de la Goma de Tara (Caesalpinia spinosa) como Ayudante en el Proceso de Coagulación-Floculación para la Remoción de Turbidez de una Suspensión Artificial de Bentonita. Información Tecnológica, 30(5), 299–308. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-07642019000500299
Zevi, Y., Dewita, S., Aghasa, A., & Dwinandha, D. (2018). Removal of Iron and Manganese from Natural Groundwater by Continuous Reactor Using Activated and Natural Mordenite Mineral Adsorption. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 111, 012016. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/111/1/012016
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Roydichan Olano-Arévalo, Angel Tuesta-Casique, Belén Azabache-Aliaga

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors retain their rights:
a. The authors retain their trademark and patent rights, as well as any process or procedure described in the article.
b. The authors retain the right to share, copy, distribute, execute and publicly communicate the article published in the Revista Amazónica de Ciencias Ambientales y Ecológicas (REACAE) (for example, place it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in the REACAE.
c. Authors retain the right to make a subsequent publication of their work, to use the article or any part of it (for example: a compilation of their works, notes for conferences, thesis, or for a book), provided that they indicate the source of publication (authors of the work, journal, volume, number and date).



