Análisis bibliométrico global sobre bacterias degradadoras de hidrocarburos en suelos entre 2018 y 2025: tendencias taxonómicas, eficiencia de biorremediación y dinámicas ecológicas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/reacae.v5i1.1342Palabras clave:
bioaumentación, biosurfactantes, consorcios microbianos, hidrocarburos del petróleo, suelos degradadosResumen
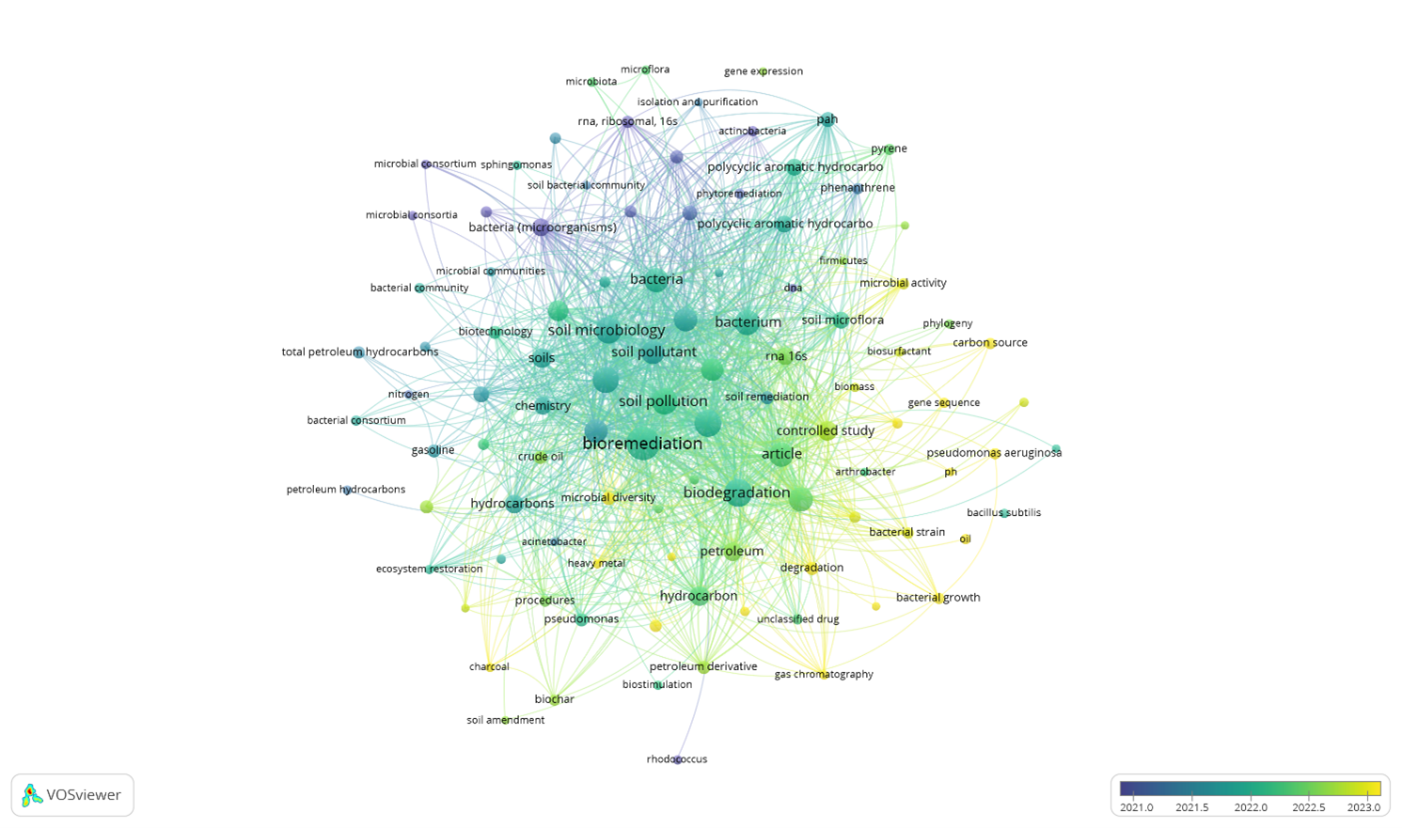
La creciente necesidad de estrategias sostenibles para tratar suelos contaminados por hidrocarburos justificó la realización de esta revisión, cuyo objetivo fue analizar bibliométricamente la producción científica global sobre bacterias degradadoras de hidrocarburos en suelos durante el periodo 2018–2025. Se aplicó una metodología de revisión sistemática-documental basada en la recopilación, depuración y normalización de cien artículos indexados en Scopus y Web of Science, cuyos metadatos fueron procesados mediante VOSviewer para evaluar patrones de colaboración, coocurrencia de palabras clave y tendencias temáticas. El análisis mostró que la investigación incrementó su producción a partir de 2020, destacándose líneas relacionadas con la bioaumentación, el uso de consorcios autóctonos, biosurfactantes y biochar para mejorar la degradación de TPH y fracción diésel. Asimismo, géneros como Pseudomonas, Bacillus, Rhodococcus y Sphingomonas presentaron las mayores frecuencias y conexiones temáticas. Los resultados también revelaron brechas vinculadas a la escasa estandarización de ensayos cinéticos y a la limitada validación en campo. En conclusión, la revisión permitió identificar tendencias, vacíos de conocimiento y oportunidades de investigación, confirmando la importancia de integrar enfoques microbianos, ecológicos y tecnológicos para optimizar la biorremediación de suelos contaminados con hidrocarburos.
Descargas
Citas
Abbas, R. I., & Flayeh, H. M. (2024). Enhanced bioremediation of diesel oil contaminants in soil. Nativa, 12(2), 359-369. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.31413/nat.v12i2.17526
Abdel-Razek, A. S., El-Sheikh, H. H., Suleiman, W. B., Taha, T. H., & Mohamed, M. K. (2020). Bioelimination of phenanthrene using degrading bacteria isolated from petroleum soil: Safe approach. Desalination and Water Treatment, 181, 131-140. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2020.25109
Abubakar, A., Abioye, O. P., Aransiola, S. A., Maddela, N. R., & Prasad, R. (2024). Crude oil biodegradation potential of lipase produced by Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hydrocarbon contaminated soil. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, 6, 26-32. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enceco.2023.12.001
Adeleye, A. O., Yerima, M. B., Nkereuwem, M. E., Onokebhagbe, V. O., Shiaka, G. P., Amoo, A. O., Asaju, C. I., Yalwaji, B., & Ishaq, S. M. (2022). Effect of bacterial co-culture and organic amendments on the bioremediation of hydrocarbons in a soil contaminated with spent engine oil. Engenharia Sanitaria e Ambiental, 27(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascibiolsci.v44i1.62289
Aladwan, M. M., Dababneh, B. F., Farah, H. S., & Abusalah, M. A. H. (2024). Identification of Oil Degrading Bacteria from Oil-Contaminated Soil in the Northeastern Part of Jordan. Inzynieria Ekologiczna, 25(5), 306-320. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.12911/22998993/186502
Al-Dhabaan, F. A. (2019). Morphological, biochemical and molecular identification of petroleum hydrocarbons biodegradation bacteria isolated from oil polluted soil in Dhahran, Saud Arabia. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 26(6), 1247-1252. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.05.029
Al-Hisnawi, A. A., Yasser, Y. K., Kadhum, N. H., & Mustafa, J. M. (2022). Hydrocarbon degradation test among the microbial community in oil-contaminated soil of power generators in Kerbala city, Iraq. Iraqi Journal of Science, 63(7), 2900-2913. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2022.63.7.14
Ali, M. F., M-Ridha, M. J., & Taly, A. H. (2018). Optimization kerosene bio-degradation by a local soil bacterium isolate Klebsiella pneumoniae Sp. Pneumonia. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 12(4), 2049-2057. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.12.4.41
Almazan-Casteñada, P. J., Alarcón, A., García-Barradas, Ó., Mendarte-Alquisira, C., & Ferrera-Cerrato, R. (2024). Phytotoxicity and phytoremediation of a gasoline-contaminated soil utilizing sunflower plants assisted with native rhizosphere bacteria. Revista Internacional de Contaminacion Ambiental, 40, 251-262. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.20937/RICA.55039
Al-Taee, Z. M., Liqaa, Y. M., Lilo, R. A., Kadhum, A. M., Mumtaz, F., Abdulabbas, H. S., Yousif, E. M., Shaker, A. T., & Al-Kinani, M. A. A. (2025). Isolation and Identification of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Soil Contaminated with Petroleum Products. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 19(3), 1955-1961. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.19.3.22
Assil, Z., Esegbue, O., Mašek, O., Gutiérrez, T., & Free, A. (2021). Specific enrichment of hydrocarbonclastic bacteria from diesel-amended soil on biochar particles. Science of the Total Environment, 762. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143084
Basim, Y., Mohebali, G., Jorfi, S., Nabizadeh Nodehi, R., Ahmadi-Moghadam, M. A., Ghadiri, A., & Jaafarzadeh Haghighifard, N. J. (2020). Biodegradation of total petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated soils using indigenous bacterial consortium. Environmental Health Engineering and Management, 7(2), 127-133. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.34172/EHEM.2020.15
Basim, Y., Mohebali, G., Jorfi, S., Nabizadeh Nodehi, R., Ahmadi-Moghadam, M. A., Ghadiri, A., & Jaafarzadeh Haghighifard, N. J. (2022). Bacterial strains diversity in contaminated soils and their potential for bioremediation of total petroleum hydrocarbons in south west of Iran. Journal of Environmental Health Science and Engineering, 20(2), 601-608. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40201-020-00592-8
Benattouche, Z., Belkhodja, H., Bouhadi, D., & Ahmed, A. (2024). Use of Biotechnology for Environmental Decontamination: Isolation of Bacteria Degrading Hydrocarbons From Soil Contaminated With Diesel Oil. Avicenna Journal of Environmental Health Engineering, 11(2), 70-74. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.34172/ajehe.5478
Bonomo, M. G., Calabrone, L., Scrano, L., Bufo, S. A., Di Tomaso, K., Buongarzone, E., & Salzano, G. (2022). Metagenomic monitoring of soil bacterial community after the construction of a crude oil flowline. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(2). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-09637-3
Boopathy, S., Appavoo, M. S., & Radhakrishnan, I. (2021). Sunflower seed husk combined with poultry droppings to degrade petroleum hydrocarbons in crude oil-contaminated soil. Environmental Engineering Research, 26(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.361
Brzeszcz, J., Skalski, T., Jankowski, L., & Kapusta, P. (2023). How do microbial communities deal with chronic hydrocarbon presence in oil seep soils? Data from historical hand-dug oil wells. Land Degradation and Development, 34(5), 1283-1296. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.4531
Brzeszcz, J., Steliga, T., Ryszka, P., Kaszycki, P., & Kapusta, P. (2024). Bacteria degrading both n-alkanes and aromatic hydrocarbons are prevalent in soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(4), 5668-5683. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-31405-8
Çevik, P. K., Eroğlu, A. B., Yıldızlı, G., Coşan, D., Kantar, Ç., & Coral, G. (2019). Isolation and characterization of diethyl phthalate degrading bacteria from crude oil contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Biology, 40(3), 275-282. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22438/jeb/40/3/MRN-959
Chai, X., Wang, M., Fu, X., Zhang, W., Huang, Y., Germaine, K. J., & Wang, J. (2023). Shift of combined ecotoxicity index in petroleum polluted soils during a bacterial remediation. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 11. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3389/fenvs.2023.1141562
Chang, Y.-C., Shimadzu, M., Choi, D., Sarkar, O., & Venkateswar Reddy, M. (2025). An enhanced degradation of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) using adaptive laboratory methods: A sustainable approach alternates to genetic engineering. Chemosphere, 387. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2025.144654
Chen, X., Meng, R., Geng, M., Zhou, J., & Pu, Y. (2024). Removal of benzo[a]pyrene by a highly degradable microbial community immobilized by modified wheat straw biochar. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 31(59), 66742-66758. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-35717-1
Crampon, M., Cazals, F., Senechaud, J., Perrault, A., Omirbekov, S., & Colombano, S. (2025). Impact of soil washing using synthetic or biological surfactants, as liquid or foam, on long-term biodegradation potential and soil microbial biodiversity in hydrocarbon-polluted soil: An experimental study. Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances, 19. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hazadv.2025.100855
Crosby, T. M., & Stadler, L. B. (2025). Plasmid Backbone Impacts Conjugation Rate, Transconjugant Fitness, and Community Assembly of Genetically Bioaugmented Soil Microbes for PAH Bioremediation. ACS Environmental Au, 5(2), 241-252. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenvironau.4c00123
Cui, J.-Q., He, Q.-S., Liu, M.-H., Chen, H., Sun, M.-B., & Wen, J.-P. (2020). Comparative study on different remediation strategies applied in petroleum-contaminated soils. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051606
Curiel-Alegre, S., de la Fuente-Vivas, D., Khan, A. H. A., García-Tojal, J., Velasco-Arroyo, B., Rumbo, C., Soja, G., Rad, C., & Barros, R. (2024). Unveiling the capacity of bioaugmentation application, in comparison with biochar and rhamnolipid for TPHs degradation in aged hydrocarbons polluted soil. Environmental Research, 252. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.118880
da Silva Correa, H., & Maranho, L. T. (2021). The potential association of Echinochloa polystachya (Kunth) Hitchc. With bacterial consortium for petroleum degradation in contaminated soil. SN Applied Sciences, 3(1). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-04070-6
Dai, Y., Liu, R., Zhou, Y., Li, N., Hou, L., Ma, Q., & Gao, B. (2020). Fire Phoenix facilitates phytoremediation of PAH-Cd co-contaminated soil through promotion of beneficial rhizosphere bacterial communities. Environment International, 136. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105421
Dehghani, M., Taatizadeh, S. B., Samaei, M. R., Shamsedini, N., Shahsavani, S., Derakhshan, Z., & Oliveri Conti, G. O. (2018). Impact of bioaugmentation of soil with n-hexadecane-degrading bacteria and phosphorus source on the rate of biodegradation in a soil-slurry system. Global Nest Journal, 20(3), 504-511. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.30955/gnj.002607
Espinosa-López, F., Pelcastre-Guzmán, K., Cerón-Nava, A., Rivera-Noriega, A., Loza-Mejía, M. A., & Islas-García, A. (2025). Sustainable Remediation Using Hydrocarbonoclastic Bacteria for Diesel-Range Hydrocarbon Contamination in Soil: Experimental and In Silico Evaluation. Sustainability (Switzerland), 17(12). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17125535
Faisal, Z. G., Jameel, M. M., & Abdullah, O. A. (2025). Isolation and Identification of Black Oil-Degrading Bacteria From Lubricant-Contaminated Soil in Northern Baghdad, Iraq. Scientific World Journal, 2025(1). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1155/tswj/4009105
Frank, Y. A., Nikitchuk, K. L., Sapega, A. A., Luk‘yanova, E. A., Ivasenko, D. A., Kosov, A. V., Gerasimchuk, A. L., & Evseeva, N. S. (2020). Improvement of the efficiency of oil-contamined soils remediation in the natural conditions of the north tomsk region and the nearby regions by indigenous microorganisms application. Bulletin of the Tomsk Polytechnic University, Geo Assets Engineering, 331(9), 130-139. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.18799/24131830/2020/9/2815
Gan, L., Wang, J.-P., & Wu, Q.-S. (2018). Bacterial diversity change in oil-contaminated soils in Jianghan oilfield via a high-throughput sequencing technique. Biotechnology, 17(3), 128-134. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3923/biotech.2018.128.134
Gielnik, A., Péchaud, Y., Huguenot, D., Cébron, A., Esposito, G., & Van Hullebusch, E. D. (2021). Functional potential of sewage sludge digestate microbes to degrade aliphatic hydrocarbons during bioremediation of a petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil. Journal of Environmental Management, 280. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111648
Grau, L., Blaudez, D., Le Cordier, H., Fornasier, F., & Cébron, A. (2023). Taxonomic and functional responses of soil and root bacterial communities associated with poplar exposed to a contamination gradient of phenanthrene. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 99(6). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiad052
Han, L., Chen, L., Feng, Y., KUZYAKOV, Y., Chen, Q., Zhang, S., Chao, L., Cai, Y., Ma, C., Sun, K., & Rillig, M. C. (2024). Microplastics alter soil structure and microbial community composition. Environment International, 185. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2024.108508
Hu, M., Zhang, F., Li, G., Ruan, H., Li, X., Zhong, L., Chen, G., & Rui, Y. (2022). Falsochrobactrum tianjinense sp. Nov., a New Petroleum-Degrading Bacteria Isolated from Oily Soils. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph191811833
Huang, Y., Zhou, Z., Cai, Y., Li, X., Huang, Y., Hou, J., & Liu, W. (2024). Response of petroleum-contaminated soil to chemical oxidation combined with biostimulation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 282. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2024.116694
Jaafar, R. S. (2025). Microbial Solutions for Environmental Cleanup: Sphingomonas paucimobilis Role in Removing Heavy Metals and Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Jordan Journal of Biological Sciences, 18(2), 275-280. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.54319/jjbs/180208
Jayaramaiah, R. H., Egidi, E., Macdonald, C. A., Wang, J.-T., Jeffries, T. C., Mallavarapu, M., & Singh, B. K. (2022). Soil initial bacterial diversity and nutrient availability determine the rate of xenobiotic biodegradation. Microbial Biotechnology, 15(1), 318-336. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.13946
Jemli, M., Karray, F., Mansour, L., Loukil, S., Bouhdida, R., Yadav, K. K., & Sayadi, S. (2025). Wastewater biotreatment and bioaugmentation for remediation of contaminated sites at an oil recycling plant. Water Science and Technology, 91(2), 139-159. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2024.364
Jia, R., Huang, X., Dang, P., Chen, Q., Zhong, S., Fan, F., Wang, C., Song, J., Chorover, J., & Rensing, C. (2024). Fe(III) reduction mediates vanadium release and reduction in vanadium contaminated paddy soil under different organic amendments. Environment International, 193. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2024.109073
Jiang, X., Mao, Z., Zhong, L., Yu, J., & Tang, Y. (2022). Strategy to Promote the Biodegradation of Phenanthrene in Contaminated Soil by a Novel Bacterial Consortium in Slurry Bioreactors. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(9). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19095515
Jiménez-Volkerink, S. N., Vila, J., Jordán, M., Minguillón, C., Smidt, H., & Grifoll, M. (2023). Multi-Omic Profiling of a Newly Isolated Oxy-PAH Degrading Specialist from PAH-Contaminated Soil Reveals Bacterial Mechanisms to Mitigate the Risk Posed by Polar Transformation Products. Environmental Science and Technology, 57(1), 139-149. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.2c05485
Jurelevicius, D., Pereira, R. D. S., da Mota, F. F., Cury, J. C., de Oliveira, I. C., Rosado, A. S., Mason, O. U., Jansson, J. K., & Seldin, L. (2022). Metagenomic analysis of microbial communities across a transect from low to highly hydrocarbon-contaminated soils in King George Island, Maritime Antarctica. Geobiology, 20(1), 98-111. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1111/gbi.12472
Khan, S., & Jain, L. (2025). Production of Rhamnolipid using Moderate Halophilic Pseudomonas aeruginosa SH-6 isolated from a Saline Lake. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 19(2), 1049-1070. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.19.2.09
Khudur, L. S., Gleeson, D. B., Ryan, M. H., Shahsavari, E., Haleyur, N., Nugegoda, D., & Ball, A. S. (2018). Implications of co-contamination with aged heavy metals and total petroleum hydrocarbons on natural attenuation and ecotoxicity in Australian soils. Environmental Pollution, 243, 94-102. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.08.040
Kidd, P. S., Álvarez, A., Álvarez-López, V., Cerdeira-Pérez, A., Rodríguez-Garrido, B., Prieto-Fernandez, Á., & Chalot, M. (2021). Beneficial traits of root endophytes and rhizobacteria associated with plants growing in phytomanaged soils with mixed trace metal-polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contamination. Chemosphere, 277. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130272
Kim, I., Shin, K., Kim, J., Ha, E., & Choi, B. (2023). Impact of Three Chainsaw Lubricants on Forest Soil Bacterial Community, Soil Respiration and Seedling Growth. Forests, 14(12). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14122287
Korshunova, T., Kuzina, E., Mukhamatdyarova, S., Iskuzhina, M., Kulbaeva, L., & Petrova, S. (2024). Effect of Herbicide-Resistant Oil-Degrading Bacteria on Plants in Soil Contaminated with Oil and Herbicides. Plants, 13(24). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants13243560
Kridi, N., Al-Shater, M. S., & Al Zoubi, M. M. (2021). Isolation and identification of some bacterial isolates from soil contaminated with crude oil and Testing Their Effectiveness. Baghdad Science Journal, 18(4), 1476-1484. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.21123/bsj.2021.18.4(Suppl.).1476
Kuc, V., Vázquez, S., Hernández, E., Martínez Álvarez, L., Villalba Primitz, J., Mac Cormack, W. P., & Ruberto, L. (2019). Hydrocarbon-contaminated Antarctic soil: Changes in bacterial community structure during the progress of enrichment cultures with different n-alkanes as substrate. Polar Biology, 42(6), 1157-1166. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-019-02508-1
Lee, G. L. Y., Ahmad, S. A., Yasid, N. A., Zulkharnain, A., Convey, P., Wan Johari, W. L., Alias, S. A., González-Rocha, G., & Shukor, M. Y. (2018). Biodegradation of phenol by cold-adapted bacteria from Antarctic soils. Polar Biology, 41(3), 553-562. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-017-2216-y
Lee, J. G., Guo, Y., Belgodere, J. A., Al Harraq, A., Hymel, A. A., Pete, A. J., Valsaraj, K. T., Benton, M. G., Miller, M. G., Jung, J. P., & Bharti, B. (2021). Lignin-Zein Composite: Synthesis, Three-Dimensional Printing, and Microbial Degradation. ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering, 9(4), 1781-1789. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07915
Lee, K. C., Archer, S. D. J., Kansour, M. K., & Al-Mailem, D. M. (2024). Bioremediation of oily hypersaline soil via autochthonous bioaugmentation with halophilic bacteria and archaea. Science of the Total Environment, 922. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.171279
Lee, S.-Y., Yun, S. H., Lee, H., Seo, G., & Kim, S. I. (2021). Multi-omics analysis of aniline-degrading bacterium, Delftia sp. K82. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology, 12(1). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40543-021-00258-6
Lemmel, F., Maunoury-Danger, F., Leyval, C., & Cébron, A. (2019). DNA stable isotope probing reveals contrasted activity and phenanthrene-degrading bacteria identity in a gradient of anthropized soils. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 95(12). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiz181
Li, B., Liu, H., Liu, X., Han, L., Yang, J., Kang, L., Tang, L., & Qian, T. (2024). Naphthalene Enhances Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Soil and Water: Effect and Mechanism. Water (Switzerland), 16(17). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/w16172537
Li, J., Chen, Y., Qin, X., Cao, A., & Lu, A. (2022). Impact of Biochar on Rhizosphere Bacterial Diversity Restoration Following Chloropicrin Fumigation of Planted Soil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042126
Li, Y., Sanfilippo, J. E., Kearns, D., & Yang, J. Q. (2022). Corner Flows Induced by Surfactant-Producing Bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas fluorescens. Microbiology Spectrum, 10(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.03233-22
Lin, M.-S., Huang, C.-Y., Lin, Y.-C., Lin, S.-L., Hsiao, Y.-H., Tu, P.-C., Cheng, P.-C., & Cheng, S.-F. (2022). Green Remediation Technology for Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy, 12(11). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12112759
Liu, S. Y. P., Peng, X. M., Zhang, X. Y., & Yuen, B. B. H. (2021). Effects of lead on petrol degradation efficiency of bacteria isolated from soils in zhuhai, guangdong, china. Environment and Ecology Research, 9(4), 166-172. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.13189/eer.2021.090404
Lu, C., Hong, Y., Liu, J., Gao, Y., Ma, Z., Yang, B., Ling, W., & Waigi, M. G. (2019). A PAH-degrading bacterial community enriched with contaminated agricultural soil and its utility for microbial bioremediation. Environmental Pollution, 251, 773-782. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.05.044
Maki, A. A., & Al-Taee, A. M. R. (2025). Isolation and Identification of Pink-Pigmented Facultative Methylotrophic Bacteria (PPFM) from the North Rumaila Field, Iraq. Novel Research in Microbiology Journal, 9(1), 41-50. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.17582/journal.NRMJ/2025/9.1.41.50
Mamet, S. D., Jimmo, A., Conway, A., Teymurazyan, A., Talebitaher, A., Papandreou, Z., Chang, Y.-F., Shannon, W., Peak, D., & Siciliano, S. D. (2021). Soil Buffering Capacity Can Be Used to Optimize Biostimulation of Psychrotrophic Hydrocarbon Remediation. Environmental Science and Technology, 55(14), 9864-9875. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c01113
Martirosyan, V., Stavi, I., Doniger, T., Applebaum, I., Sherman, C., Levi, M., & Steinberger, Y. (2025). Bacterial Community Dynamics in Oil-Contaminated Soils in the Hyper-Arid Arava Valley. Agronomy, 15(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051198
Mauricio-Gutiérrez, A., MacHorro-Velázquez, R., Jiménez-Salgado, T., Vázquez-Cruz, C., Sánchez-Alonso, M. P., & Tapia-Hernández, A. (2020). Bacillus pumilus and Paenibacillus lautus eff ectivity in the process of biodegradation of diesel isolated from hydrocarbons contaminated agricultural soils. Archives of Environmental Protection, 46(4), 59-69. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.24425/aep.2020.135765
Medina, R., David Gara, P. M., Fernández-González, A. J., Rosso, J. A., & del Panno, M. T. (2018). Remediation of a soil chronically contaminated with hydrocarbons through persulfate oxidation and bioremediation. Science of the Total Environment, 618, 518-530. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.326
Minnikova, T., Kolesnikov, S., Minkina, T., & Mandzhieva, S. (2021). Assessment of ecological condition of haplic chernozem calcic contaminated with petroleum hydrocarbons during application of bioremediation agents of various natures. Land, 10(2), 1-20. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020169
Minnikova, T., Kolesnikov, S., Ruseva, A., Kazeev, K., Minkina, T., Mandzhieva, S., & Sushkova, S. (2022). Influence of the biochar on petroleum hydrocarbon degradation intensity and ecological condition of Haplic Chernozem. Eurasian Journal of Soil Science, 11(2), 157-166. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.18393/ejss.1037798
Mori, J. F., & Kanaly, R. A. (2020). Multispecies Diesel Fuel Biodegradation and Niche Formation Are Ignited by Pioneer Hydrocarbon-Utilizing Proteobacteria in a Soil Bacterial Consortium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 87(1), 1-19. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02268-20
Mori, J. F., Nagai, M., & Kanaly, R. A. (2021). Complete genome sequence of cupriavidus necator kk10, an azaarene-degrading and polyhydroxyalkanoate-producing soil bacterium. Microbiology Resource Announcements, 10(28). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.00423-21
Nafal, D. H., & Abdulhay, H. S. (2020). Bioremediation of petroleum polluted soils using consortium bacteria. Iraqi Journal of Science, 61(5), 961-969. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.24996/ijs.2020.61.5.3
Naloka, K., Petchsom, T., Muangchinda, C., & Pinyakong, O. (2025). A low-cost, ready-to-use Mycolicibacterium-Bacillus bioaugmentation strategy: Impacts on soil microbial community and enhanced diesel oil removal. Applied Soil Ecology, 213. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2025.106298
Nanekar, R. D., & Kokitkar, S. S. (2024). Isolation, Characterization and Optimization of Indigenous Petrol Degrading Bacteria from Oil Contaminated Soil. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology, 18(3), 2014-2023. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22207/JPAM.18.3.52
Navas-Cáceres, O. D., Parada, M., & Zafra, G. (2023). Development of a highly tolerant bacterial consortium for asphaltene biodegradation in soils. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 30(59), 123439-123451. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30682-7
Odion, E. E., Ma, J., Bräu, L., Lim, J. W., & Lin, C. (2025). Interactive effects of heavy metals and soil conditioners on rhizodegradation of long-chain petroleum hydrocarbons in soils. Environmental Pollution, 384. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2025.126995
Osinowo, I., Abioye, O. P., Oyeleke, S. B., & Oyewole, O. A. (2020). Bioremediation of diesel contaminated soil using bacterial cocktail and organic nutrients. Journal of Microbiology, Biotechnology and Food Sciences, 10(2), 150-158. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.15414/jmbfs.2020.10.2.150-158
Panwar, R., & Mathur, J. (2023). Microbial-assisted phytodegradation for the amelioration of pyrene-contaminated soil using Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Aspergillus oryzae with alfalfa and sunflower. 3 Biotech, 13(7). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03664-2
Posada-Baquero, R., Jiménez-Volkerink, S. N., García, J. L., Vila, J., Cantos, M., Grifoll, M., & Ortega- Calvo, J. J. (2020). Rhizosphere-enhanced biosurfactant action on slowly desorbing PAHs in contaminated soil. Science of the Total Environment, 720. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137608
Roszak, M., Honselmann genannt Humme, J., Stachurska, X., Dubrowska, K., Kajdanowicz, J., Gołębiewska, M., Kiepas-Kokot, A., Osińska, B., Augustyniak, A., & Karakulska, J. (2021). Development of an autochthonous microbial consortium for enhanced bioremediation of pah-contaminated soil. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(24). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222413469
Sato, K., Take, S., Ahmad, S. A., Gomez-Fuentes, C., & Zulkharnain, A. (2023). Carbazole Degradation and Genetic Analyses of Sphingobium sp. Strain BS19 Isolated from Antarctic Soil. Sustainability (Switzerland), 15(9). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15097197
Sattar, S., Siddiqui, S., Shahzad, A., Bano, A., Naeem, M., Hussain, R., Khan, N., Jan, B. L., & Yasmin, H. (2022). Comparative Analysis of Microbial Consortiums and Nanoparticles for Rehabilitating Petroleum Waste Contaminated Soils. Molecules, 27(6). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27061945
Shen, Y., Ji, Y., Li, C., Luo, P., Wang, W., Zhang, Y., & Nover, D. (2018). Effects of phytoremediation treatment on bacterial community structure and diversity in different petroleum-contaminated soils. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 15(10). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15102168
ShirzadianGilan, R., Parvizi, Y., Pazira, E., & Rejali, F. (2023). Remediation capacity of drought-tolerant plants and bacteria in petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil in Iran. South African Journal of Botany, 153, 1-10. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2022.12.014
Steliga, T., Wojtowicz, K., Kapusta, P., & Brzeszcz, J. (2020). Assessment of biodegradation efficiency of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) in soil using three individual bacterial strains and their mixed culture. Molecules, 25(3). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030709
Subramaniam, K., Shaharuddin, N. A., Tengku-Mazuki, T. A., Zulkharnain, A., Khalil, K. A., Convey, P., & Ahmad, S. A. (2020). Statistical optimisation for enhancement of phenol biodegradation by the Antarctic soil bacterium Arthrobacter sp. Strain AQ5-15 using response surface methodology py. Journal of Environmental Biology, 41(6), 1560-1569. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.22438/JEB/41/6/MRN-1496
Sydow, M., Owsianiak, M., Framski, G., Woźniak-Karczewska, M., Piotrowska-Cyplik, A., Ławniczak, Ł., Szulc, A., Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A., Heipieper, H. J., & Chrzanowski, Ł. (2018). Biodiversity of soil bacteria exposed to sub-lethal concentrations of phosphonium-based ionic liquids: Effects of toxicity and biodegradation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 147, 157-164. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.08.026
Taher, A. M., & Saeed, I. O. (2022). Bioremediation of Contaminated Soil with Crude Oil Using New Genus and Species of Bacteria. Journal of King Abdulaziz University, Marine Science, 32(2), 13-35. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.4197/Mar.32-2.2
Thomas, F., Corre, E., & Cébron, A. (2019). Stable isotope probing and metagenomics highlight the effect of plants on uncultured phenanthrene-degrading bacterial consortium in polluted soil. ISME Journal, 13(7), 1814-1830. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0394-z
Vauloup, A., & Cébron, A. (2025). Development of a device to trap soil bacteria capable of degrading organic contaminants such as alkanes and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 491. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137690
Wang, J., Su, X., Zhang, C., Han, Z., & Wang, M. (2025). Biodegradation of Benzo(a)pyrene in Contaminated Soil: Plant and Microorganism Contributions from Isotope Tracing. Toxics, 13(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050405
Wang, P., Liu, T., Liu, J., Duan, Y., Han, S., Zhang, Z., Li, L., & Lin, Y. (2022). Effects of different colored polyethylene mulching films on bacterial communities from soil during enrichment incubation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 246. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.114160
Wang, W., Gao, Y., Du, J., Zheng, L., Kong, X., Wang, H., Yang, X., Duan, L., Zhao, Q., Liu, Y., & Naidu, R. (2023). Dose–effect of nitrogen regulation on the bioremediation of diesel contaminated soil. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 32. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103245
Xia, M., Chakraborty, R., Terry, N., Singh, R. P., & Fu, D. (2020). Promotion of saltgrass growth in a saline petroleum hydrocarbons contaminated soil using a plant growth promoting bacterial consortium. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 146. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104808
Yessentayeva, K., Reinhard, A., Berzhanova, R., Mukasheva, T., Urich, T., & Mikolasch, A. (2024). Bacterial crude oil and polyaromatic hydrocarbon degraders from Kazakh oil fields as barley growth support. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 108(1). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-024-13010-y
Yu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, N., Guo, J., Xu, W., Ma, M., & Li, X. (2020). Remediation of crude oil-polluted soil by the bacterial rhizosphere community of suaeda salsa revealed by 16S rRNA genes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17051471
Yuan, S., Friman, V.-P., Balcázar, J. L., Zheng, X., Ye, M., Sun, M., & Hu, F. (2023). Viral and Bacterial Communities Collaborate through Complementary Assembly Processes in Soil to Survive Organochlorine Contamination. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 89(3). Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.01810-22
Zhang, Y., Qian, F., & Bao, Y. (2025). Variations of microbiota and metabolites in rhizosphere soil of Carmona microphylla at the co-contaminated site with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 290. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2025.117734
Zhu, H., Ren, L., Yang, H., & Zhang, J. (2025). Leveraging indigenous Bacillus consortia for heavy oil biodegradation and soil bioremediation. Environmental Technology and Innovation, 40. Scopus. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2025.104415
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2026 Emmir Oswaldo Chavez-Cayo

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución 4.0.
Los autores retienen sus derechos:
a. Los autores retienen sus derechos de marca y patente, y tambien sobre cualquier proceso o procedimiento descrito en el artículo.
b. Los autores retienen el derecho de compartir, copiar, distribuir, ejecutar y comunicar públicamente el articulo publicado en la Revista Amazónica de Ciencias Ambientales y Ecológicas (REACAE) (por ejemplo, colocarlo en un repositorio institucional o publicarlo en un libro), con un reconocimiento de su publicación inicial en la REACAE.
c. Los autores retienen el derecho a hacer una posterior publicación de su trabajo, de utilizar el artículo o cualquier parte de aquel (por ejemplo: una compilación de sus trabajos, notas para conferencias, tesis, o para un libro), siempre que indiquen la fuente de publicación (autores del trabajo, revista, volumen, número y fecha).



