Effect of liming on forage yield and profitability of INIAP 543 – QPM corn in an Andisol soil in Ecuador
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.51252/raa.v5i1.760Keywords:
economic benefit, soil liming, forage yield, acidic soil, Zea maysAbstract
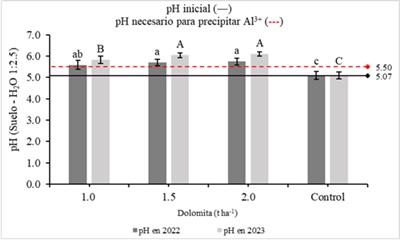
Forage corn is essential for ruminant production; however, the acidity of the soil significantly reduces its productivity. The aim of this work was to evaluate the effect of liming on the forage yield and profitability of INIAP 543 – QPM corn grown in an andisol soil of Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas, Ecuador. Four treatments consisting of three doses of dolomite (1.0, 1.5 and 2.0 t ha-1) and a control treatment without lime were evaluated. The variables recorded were green matter yield, final soil pH and net economic profit. Liming had a significant impact (p<0.05) on green mass yield and final soil ph. The dose of 1.5 t ha-1 of dolomite showed the greatest increase in green matter yield. All liming doses succeeded in raising pH above 5.5, which is necessary to precipitate Al3+. The 1.5 t ha-1 dose of dolomite resulted in the greatest net economic profit from liming. In conclusion, the 1.5 t ha-1 dose of dolomite lime is agronomically and economically viable to enhance corn forage production on acid andisol soil.
Downloads
References
Abril, C., Gallardo, E., Robles Carrillo, A. M., Albán, A., & Toainga, S. (2020). Potencial geológico del Alófano en la provincia de Santo Domingo de los Tsáchilas. FIGEMPA: Investigación y Desarrollo, 1(1), 79-92. https://doi.org/10.29166/revfig.v1i1.2290
Agegnehu, G., Amede, T., Erkossa, T., Yirga, C., Henry, C., Tyler, R., Nosworthy, M. G., Beyene, S., & Sileshi, G. W. (2021). Extent and management of acid soils for sustainable crop production system in the tropical agroecosystems: a review. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica, Section B — Soil & Plant Science, 71(9), 852-869. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2021.1954239
Analuisa Aroca, I. A., Guerrero-Casado, J., Fernández Gallardo, J. A., & Rodríguez Ulcuango, O. M. (2020). Caracterización socioeconómica del agricultor maicero en la Provincia de Manabí mediante técnicas de análisis multivariantes. Podium, 38, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.31095/podium.2020.38.1
Ayvar-Serna, S., Díaz-Nájera, J. F., Vargas-Hernández, M., Mena-Bahena, A., Tejeda-Reyes, M. A., & Cuevas-Apresa, Z. (2020). Rentabilidad de sistemas de producción de grano y forraje de híbridos de maíz, con fertilización biológica y química en trópico seco. REVISTA TERRA LATINOAMERICANA, 38(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.28940/terra.v38i1.507
Blackmore, I., Rivera, C., Waters, W. F., Iannotti, L., & Lesorogol, C. (2021). The impact of seasonality and climate variability on livelihood security in the Ecuadorian Andes. Climate Risk Management, 32, 100279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crm.2021.100279
Cavache Ulloa, M. (2016). El suelo y la productividad agricola. XIV Congreso Ecuatoriano de la Ciencia del Suelo EL, 0(0), 1-28. https://www.academia.edu/9324382/LOS_SUELOS_DEL_ECUADOR.
Chairiyah, R. R., Ramija, K. E., & Batubara, S. F. (2021). Liming of acid soil and the interaction with soil pH and corn productivity. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 807(4), 042071. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/807/4/042071
Correndo, A., & García, F. (2012). Concentración de nutrientes en planta como herramienta de diagnóstico: Cultivos extensivos. Informaciones Agronómicas, 5(February), 1-8. http://lacs.ipni.net/article/LACS-1155
Crusciol, C. A. C., Artigiani, A. C. C. A., Arf, O., Carmeis Filho, A. C. A., Soratto, R. P., Nascente, A. S., & Alvarez, R. C. F. (2016). Soil fertility, plant nutrition, and grain yield of upland rice affected by surface application of lime, silicate, and phosphogypsum in a tropical no-till system. CATENA, 137, 87-99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.09.009
Crusciol, C. A. C., Marques, R. R., Carmeis Filho, A. C. A., Soratto, R. P., Costa, C. H. M., Ferrari Neto, J., Castro, G. S. A., Pariz, C. M., Castilhos, A. M., & Franzluebbers, A. J. (2019). Lime and gypsum combination improves crop and forage yields and estimated meat production and revenue in a variable charge tropical soil. Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 115(3), 347-372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10705-019-10017-0
Daba, N. A., Li, D., Huang, J., Han, T., Zhang, L., Ali, S., Khan, M. N., Du, J., Liu, S., Legesse, T. G., Liu, L., Xu, Y., Zhang, H., & Wang, B. (2021). Long-Term Fertilization and Lime-Induced Soil pH Changes Affect Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Grain Yields in Acidic Soil under Wheat-Maize Rotation. Agronomy, 11(10), 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11102069
Devkota, S., Panthi, S., & Shrestha, J. (2019). Evaluation of maize varieties in acid soil condition. Agrica, 8(2), 128. https://doi.org/10.5958/2394-448X.2019.00018.X
Dugalić, M., Životić, L., Gajić, B., & Latković, D. (2023). Small Doses of Lime with Common Fertilizer Practices Improve Soil Characteristics and Foster the Sustainability of Maize Production. Agronomy, 14(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14010046
Enesi, R. O., Dyck, M., Chang, S., Thilakarathna, M. S., Fan, X., Strelkov, S., & Gorim, L. Y. (2023). Liming remediates soil acidity and improves crop yield and profitability - a meta-analysis. Frontiers in Agronomy, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fagro.2023.1194896
Erenstein, O., Jaleta, M., Sonder, K., Mottaleb, K., & Prasanna, B. M. (2022). Global maize production, consumption and trade: trends and R&D implications. Food Security, 14(5), 1295-1319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-022-01288-7
Espinosa, J., & Molina, E. (1999). Acidez y Encalado de Suelos, Libro Por J Espinosa y E Molina (1.a ed.). International Plant Nutrition Institute.
Fiantis, D., Ginting, F., Gusnidar, Nelson, M., & Minasny, B. (2019). Volcanic Ash, Insecurity for the People but Securing Fertile Soil for the Future. Sustainability, 11(11), 3072. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11113072
INEC. (2024). Módulo de Información Ambiental y Tecnificación Agropecuaria, ESPAC 2023 (p. 27). Instituto Nacional de Estadísticas y Censo. https://www.ecuadorencifras.gob.ec/informacion-agroambiental/
Kasno, A., Nurida, N., Siregar, A. F., Samsun, A., Widowati, L. R., & Husnain. (2023). Enhancing chemical properties and maize yield through dolomite application on rock phosphate-amended oxisol. E3S Web of Conferences, 467, 01002. https://doi.org/10.1051/e3sconf/202346701002
Kisić, I., Ćorić, R., Lončarić, Z., Jurković, D., Kajić, N., Ćorić, A., Jurina, D., & Delač, D. (2021). Effectiveness of different liming materials on some soil properties and yield of crops. Journal of Central European Agriculture, 22(2), 346-360. https://doi.org/10.5513/JCEA01/22.2.3171
Krismawati, A., Latifah, E., & Sugiono. (2022). Effectiveness of Dolomite on Growth and Yield of Maize (Zea mays l.) in Dry Land. https://doi.org/10.2991/absr.k.220102.002
Li, Y., Cui, S., Chang, S. X., & Zhang, Q. (2019). Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: a global meta-analysis. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 19(3), 1393-1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2120-2
Limongi Andrade, R., Alarcón Cobeña, D., & Zambrano Zambrano, E. (2019). Variedad INIAP 543-QPM con la calidad de proteína para el consumo en choclo en el litoral ecuatoriano (p. 2). INIAP.
MAG. (2022). Boletín situacional del cultivo de maíz. Coordinación general de información nacional agropecuaria (p. 6). Ministerio de Agricultura y Ganadería. http://sipa.agricultura.gob.ec/boletines/situacionales/2022/boletin_situacional_maiz_duro_2022.pdf
Mihai, R. A., Melo Heras, E. J., Terán Maza, V. A., Espinoza Caiza, I. A., Pinto Valdiviezo, E. A., & Catana, R. D. (2023). The Panoramic View of Ecuadorian Soil Nutrients (Deficit/Toxicity) from Different Climatic Regions and Their Possible Influence on the Metabolism of Important Crops. Toxics, 11(2), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11020123
Mite, F., Medina, L., & Espinosa, J. (2009). Efecto de la corrección del pH en el rendimiento de piña en suelos volcánicos. Informaciones Agronómicas, 73, 1-5. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320981814_Efecto_de_la_correccion_del_pH_en_el_rendimiento_de_pina_en_suelos_volcanicos
Pérez López, A. E., Martínez Bustamante, E., Vélez Vargas, L. D., & Cotes Torres, J. M. (2013). Acumulación y distribución de fitomasa en el asocio de maíz (zea mays l.) y fríjol (phaseolus vulgaris l.) / biomass accumulation and distribution in associated crop of maize (zea mays l.) and bean (phaseolus vulgaris l.). Revista Facultad Nacional de Agronomía Medellín, 66(1), 16. https://repositorio.unal.edu.co/handle/unal/72967
Rahman, S. U., Han, J.-C., Ahmad, M., Ashraf, M. N., Khaliq, M. A., Yousaf, M., Wang, Y., Yasin, G., Nawaz, M. F., Khan, K. A., & Du, Z. (2024). Aluminum phytotoxicity in acidic environments: A comprehensive review of plant tolerance and adaptation strategies. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 269, 115791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115791
Razquin, C. J., Maddonni, G. A., & Vega, C. R. C. (2017). Estimación no destructiva del área foliar en plantas individuales de maíz (Zea mays L.) creciendo en canopeos. AgriScientia, 34(1), 27. https://doi.org/10.31047/1668.298x.v34.n1.17356
Silva-Yumi, J., Cazorla Martínez, R., Medina Serrano, C., & Chango Lescano, G. (2021). Alofán, una nanopartícula natural presente en andisoles del Ecuador, propiedades y aplicaciones. La Granja, 33(1), 53-66. https://doi.org/10.17163/lgr.n33.2021.05
Tabri, F., Syafruddin, Aqil, M., & Herawati. (2021). The effect of sulphur and lime dosage application on grain yield of hybrid maize. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 911(1), 012036. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/911/1/012036
Takahashi, T. (2020). The diversity of volcanic soils: focusing on the function of aluminum–humus complexes. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 66(5), 666-672. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2020.1769453
Victoria, O., Ping, A., Yang, S., & Eneji, E. (2019). Liming and Nitrogen Effects on Maize Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 50(16), 2041-2055. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103624.2019.1648663
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jessica Elizabeth Cargua-Chávez, Mirian Susana Aguila-Lombeida, Lisseth Katherine Moreno-Armijos, Kevin Eligio Intriago-Loor, Ana María Párraga-Vera, Galo Alexander Cedeño-García, Benny Alexander Avellan-Cedeño, Geoconda Aracely López-Álava, Katty Paola Ormaza-Cedeño

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
The authors retain their rights:
a. The authors retain their trademark and patent rights, as well as any process or procedure described in the article.
b. The authors retain the right to share, copy, distribute, execute and publicly communicate the article published in the Revista Agrotecnológica Amazónica (RAA) (for example, place it in an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgment of its initial publication in the RAA.
c. Authors retain the right to make a subsequent publication of their work, to use the article or any part of it (for example: a compilation of their works, notes for conferences, thesis, or for a book), provided that they indicate the source of publication (authors of the work, journal, volume, number and date).





